Introdution to staģes
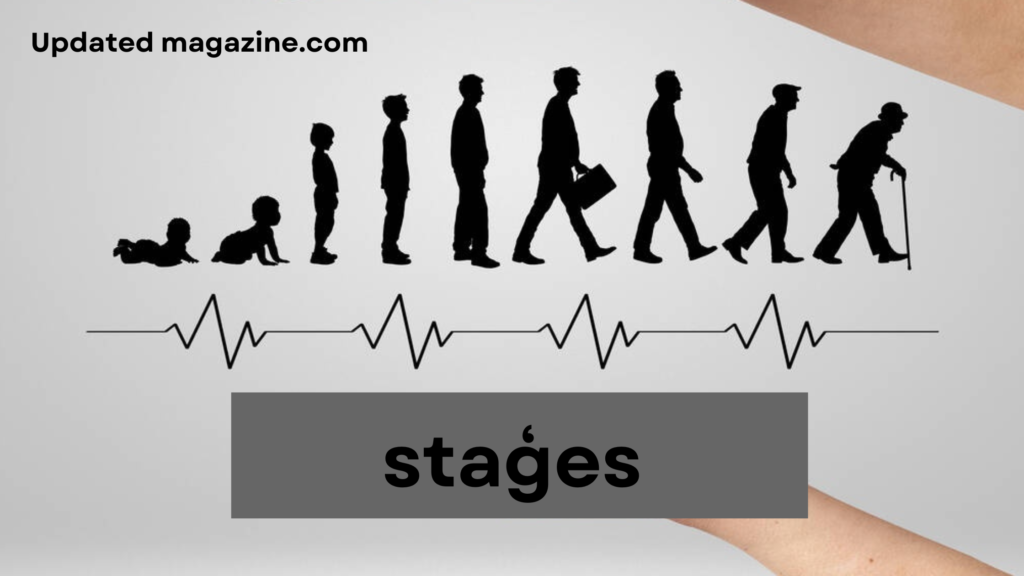
The concept of “staģes” refers to the various phases of life that individuals undergo as they grow and develop, encompassing psychological, emotional, and social transformations. According to Erik Erikson’s theory, there are eight distinct stages of life, each marked by specific psychosocial crises that must be resolved for healthy development. These stages include infancy, early childhood, preschool years, school age, adolescence, young adulthood, middle adulthood, and late adulthood. Understanding these stages is vital for personal growth and relationship dynamics, as it helps individuals navigate life’s challenges, align their goals with their current phase, and foster meaningful connections.
The Eight staģes of Life
According to developmental psychologist Erik Erikson, there are eight staģes of life, each characterized by specific psychosocial crises that individuals must resolve to progress to the next stage. These staģesare:
- Infancy (0-18 months): Trust vs. Mistrust
- Early Childhood (18 months-3 years): Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
- Preschool Years (3-5 years): Initiative vs. Guilt
- School Age (6-11 years): Industry vs. Inferiority
- Adolescence (12-18 years): Identity vs. Role Confusion
- Young Adulthood (19-40 years): Intimacy vs. Isolation
- Middle Adulthood (40-65 years): Generativity vs. Stagnation
- Late Adulthood (65+ years): Ego Integrity vs. Despair
The Significance of Understanding Stages
Understanding the staģes of life is crucial for several reasons:
- Personal Growth: By recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities presented in each stage, individuals can better navigate their personal growth and development.
- Relationship Dynamics: Comprehending the emotional and social changes that occur during different staģes can help individuals build stronger, more meaningful relationships.
- Goal Setting: Aligning personal goals with the current stage of life can lead to greater satisfaction and fulfillment.
- Adaptability: Recognizing that life is a series of staģes can help individuals adapt more effectively to changes and transitions.
Infancy and Early Childhood
The first two staģes of life, infancy and early childhood, are crucial for the development of trust, autonomy, and basic skills. During these stages, children rely heavily on caregivers for their physical and emotional needs, forming the foundation for future relationships and emotional well-being.
Key milestones during this period include:
- Learning to trust caregivers and the world around them
- Developing a sense of autonomy and independence
- Acquiring basic motor skills and language
- Engaging in imaginative play and social interactions
Childhood and Adolescence
The school age and adolescent staģes are marked by significant cognitive, emotional, and social changes. Children begin to develop a sense of industry and competence as they navigate the challenges of formal education and social relationships.
During adolescence, individuals grapple with their sense of identity, exploring different roles and values. This stage is often characterized by increased independence, emotional turmoil, and the formation of intimate relationships outside the family.
Key milestones during this period include:
- Developing a sense of industry and competence
- Forming friendships and navigating social dynamics
- Exploring personal interests and hobbies
- Establishing a sense of identity and independence
- Experiencing physical and hormonal changes
Adulthood
The adult staģes of life, including young adulthood, middle adulthood, and late adulthood, involve significant personal and professional responsibilities. These staģes are characterized by the pursuit of intimacy, generativity, and ego integrity.
In young adulthood, individuals often focus on establishing personal and economic independence, pursuing higher education and career goals, and forming significant relationships. Middle adulthood is marked by increased responsibilities, such as managing a family, career, and possibly caring for aging parents. Late adulthood involves reflection on life experiences and finding meaning in one’s existence.
Key milestones during this period include:
- Establishing personal and economic independence
- Pursuing higher education and career goals
- Forming significant relationships and starting a family
- Managing increased personal and professional responsibilities
- Reflecting on life achievements and finding meaning in one’s existence
The Importance of Transitions
Transitions between staģes can be challenging, but they also present opportunities for growth and self-discovery. Recognizing the importance of these transitions can help individuals navigate them more effectively.
Some strategies for managing transitions include:
- Seeking support from friends, family, or professionals
- Engaging in self-reflection and personal growth activities
- Setting realistic goals and expectations for the new stage
- Embracing change and uncertainty as part of the journey
Conclusion
Understanding the staģes of life is essential for personal growth, relationship dynamics, and overall well-being. By recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities presented in each stage, individuals can better navigate their journey through life. Remember, each stage is a valuable part of the human experience, and embracing the changes and transitions that come with them can lead to a more fulfilling and enriched life.
Also Read: Suwuianna: Unlocking Inner Strength
FAQs
What are the benefits of understanding the staģes of life?
Understanding the staģes of life can help individuals:
- Align personal goals with the current stage of life
- Adapt more effectively to changes and transitions
- Build stronger, more meaningful relationships
- Engage in personal growth and development
How can individuals manage transitions between stages?
Strategies for managing transitions include:
- Seeking support from friends, family, or professionals
- Engaging in self-reflection and personal growth activities
- Setting realistic goals and expectations for the new stage
- Embracing change and uncertainty as part of the journey
Is it possible to skip or repeat staģes in life?
While the staģes of life are generally sequential, it is possible for individuals to experience certain staģes out of order or to repeat staģes due to unique circumstances or personal choices. However, the core developmental tasks and challenges associated with each stage remain relevant.
Can understanding the staģesof life help in career planning?
Yes, understanding the staģes of life can inform career planning and decision-making. For example, individuals in young adulthood may prioritize exploring different career paths, while those in middle adulthood may focus on career advancement and stability.
How does culture influence the staģes of life?
Culture can shape the expectations, timelines, and experiences associated with each stage of life. For example, cultural norms and values may influence the timing and nature of significant life events, such as marriage, parenthood, or retirement.